Full Text Indexing
Within Umbria, full text indexing is a key component of the database and schema to index, lookup and order data to be returned in the Umbria user interface quickly and efficiently. Samples of data that gets full text indexed are descriptions, names, entities, and marketing content. It is key that these catalogs are properly maintained in SQL Server for the performance of Umbria searches, and pages.
Diagnosing Performance and Checking Full Text Indices
If performance is lagging in your searches to return results, especially when searching for descriptors, or date ranges or other content, and is taking longer than 5 seconds; you may have a full text index problem.
The following searches could use full text indexes for the page content returned:
- Matter search
- Client search
- Budget searches
- Price Search
- Scorecard search
- Practice group Performance pieces
To see if full text indexing is the cause of the system’s poor performance, you’ll need administrative access to the Umbria SQL server to run the below queries:
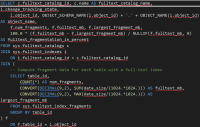
Query 1: Basic count of Fragments

This query allows you to see from the full text catalog, the number of fragments there are in the catalog. For any database, including Umbria, this number should be less than 10. Typically with most heavily used Umbria environments, this number will be 1-5, if these indexes are maintained regularly. If these indexes, are not maintained, this number could grow to 20-100.
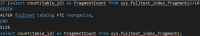
Query 2: A more advanced Query: The catalog sizes, and amount fragmented
This query allows database administrators to pinpoint fragmentation easier, and find out the amount of fragmentation there is in the full text index. Key columns are Num_fragments (number of fragments like the simple query above), fulltext_mb (size of full text file), largest_fragment_mb (largest fragmented portion), and fulltext_fragmentation_in_percent (calculates the percent fragmented).
If the fragmentation percent is over 15%, your full text queries will have some performance hindrances.
Solving Full Text Catalog Fragmentation and Maintenance
When your full text index is fragmented, it should be reorganized. Unfortunately, in SQL Server all versions 2005 and higher, full text indexes are not included in the rebuild and reorganize functions of the Maintenance Plan Wizards. These need to be set up as scripted jobs that run.
To set up these jobs, you should have SQL Server Agent installed and running on the SQL Server.
For best optimization, this should be run at least weekly but could be scheduled daily, as the job will have a check on the fragment count, and if it does not meet the criteria, it will not execute a reorganization.
This process, if normally scheduled can take up to 2 minutes, and if the first time running it, can take 5-10 minutes depending on your SQL server hardware, and how bad the fragmentation is.
Create a new job that runs the following SQL statement:
What this job will do, is that if fragments are over 10 in number, it will process the reorganization of the full text index catalog. If this criteria is not met, it will simply show the count of fragments.